We have provided you with Extra and Important Questions from Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes. This Extra and Important Questions will help you to score 100% in your Board Exams. These extra questions will be helpful to revise the important topics and concepts.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.
Table of Contents
Life Processes Class 10 Important Questions with Answers Science Chapter 6
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Very Short Answer Type
Question:What will happen to a plant if its xylem is removed? [CBSE 2009]
Answer:
Xylem helps in the transport of water and minerals to the various parts of the plant. If xylem is removed it would ultimately lead to the death of the plant.
Question:Name the green dot like structures in some cells observed by a student when a leaf peel was viewed under a microscope. What is the green colour due to? [CBSE 2010]
Answer:
The green dots like structures seen are the chloroplasts. The green colour is due to the pigment called chlorophyll.
Question:Give one reason why multicellular organisms require special organs for exchange of gases between their body and their environment. [CBSE 2010]
Answer:
Simple diffusion is not sufficient for the exchange of gases in multicellular organisms as all their cells are not in direct contact with the environment. So, they require special organs for exchange of gases between their body and their environment.
Question:What process in plants is known as transpiration? [CBSE 2008]
Answer:The loss of water in the form of vapour from the aerial parts of the plant is known as transpiration.
Question:What is osmoregulation? [CBSE 2006]
Answer:
The maintenance of optimum concentration of water and salts (electrolytes) in the body fluids is called as osmoregulation.
Question:Why is carbon dioxide mostly transported in dissolved form?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide is mostly transported in the dissolved form as it is more soluble in water.
Question:When we breathe out, why does the air passage not collapse? [CBSE 2014]
Answer:
Rings of cartilage present on trachea prevent it from collapsing during the passage of air.
Question:Herbivores have longer small intestine while carnivores have shorter small intestine. Give reason. [CBSE 2014]
Answer:
Herbivores have a longer small intestine compared to the carnivores to allow time for the cellulose present in the grass to get digested.
Question:Mention the respiratory unit of lungs and excretory unit of kidneys. [CBSE 2014]
Answer:
The respiratory unit of lungs are alveoli and excretory unit of kidneys are nephrons.
Question:Some organisms derive nutrition from plants or animals without killing them. What are these organisms called? Write one example. [CBSE 2014]
Answer:
They are called parasites, e.g. Cuscuta and tapeworm are the parasites of plants and animals respectively.
Question:What are the major constituents of urine? [CBSE 2008]
Answer:
Urine is an aqueous solution of water, urea, chloride, sodium, potassium, creatinine and other dissolved ions, inorganic and organic compounds (proteins, hormones, and metabolites).
Question:Where does the urine produced by the kidneys get stored? [CBSE 2006]
Answer:
Urinary bladder.
Question:How does transpiration help in upward transport of substances? [CBSE 2008]
Answer:
Transpiration creates a suction pressure which pulls up water along with the minerals through the xylem.
Question:When the right atrium contract, blood flows from it to which part of the heart? [CBSE 2007]
Answer:
Right ventricle.
Question:Write the functions of the two upper chambers of the human heart. [CBSE 2011]
Answer:The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from various parts of the body through the vena cava.
The left atrium receives the oxygenated blood from the lungs through the pulmonary artery.
Question:Leakage of blood from vessels reduces the efficiency of pumping system. How is the leakage prevented? [CBSE 2010, 2011]
Answer:
Leakage is prevented by the blood platelets present in the blood which help in clotting the blood at the site of injury.
Question:Why are valves present in heart and the veins? [CBSE 2010,2011]
Answer:
Valves present in the heart does not allow the blood to flow backwards when the atria or ventricles contracts. Valves are present in the veins to prevent the back flow of blood in the veins as it travels at very slow rate in the veins.
Question:Which mechanism plays an important role in transportation of water in plants
(i) During daytime
(ii) At night? [CBSE 2011, 2012]
Answer:During daytime – Transpiration; At Night – Root pressure.
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Short Answer Type
Question:How are the fats digested in our bodies? Where does this process take place? [CBSE 2011]
Answer:
Bile juice produced by the liver breaks down the large fat globules into smaller globules by the process of emulsification. These small globules are then digested by the fat digesting enzymes. This process takes place in the small intestine.
Question:State the function of the epiglottis. [CBSE 2004]
Answer:
Epiglottis covers the opening of the wind pipe (the glottis) and prevents the entry of food into the wind pipe during swallowing.
Question:The breathing cycle is rhythmic, whereas exchange of gases is a continuous process. Comment upon this statement.
Answer:
Some volume of air called as residual volume is left behind in the lungs even after forceful breathing out of air. This helps to provide sufficient time for oxygen to be absorbed and for carbon dioxide to be released. Even in the absence of continuous breathing, the exchange of these gases is continuous. Hence, breathing cycle is rhythmic, whereas exchange of gases is a continuous process.
Question:What are the end products formed during fermentation in yeast? Under what condition a similar process takes place in our body that lead to muscle cramps? [CBSE 2010]
Answer:
The end products formed during fermentation in yeast are ethanol and carbon dioxide. A similar process occurs in the muscles and produces lactic acid during anaerobic respiration in the muscles. Accumulation of lactic acid in the muscle cells lead to muscular cramps.
Question:Give Reasons:
(a) Rings of cartilage are present in the trachea.
(b) Lungs always contain a residual volume of air. [CBSE 2013]
Answer:(a) The walls of trachea have rings of cartilage on them which prevent it from collapsing.
(b) The volume of air left behind in the lungs even after forceful breathing out of air is called as residual volume. This helps to provide sufficient time for oxygen to be absorbed and for the carbon dioxide to be released.
Question:State in brief the role of lungs in the exchange of gases. [CBSE 2012]
Answer:
Lungs have alveoli which provide a larger surface for exchange of gases and are richly supplied with blood vessels to enable faster exchange. So, lungs help in providing oxygen to various tissues of the body and removal of carbon dioxide from the body.
Question:What is the basic unit of kidney called? Why is it composed of very thin blood capillaries? [CBSE 2015]
Answer:
The basic unit of kidney is called nephron. It is composed of a cluster of very thin blood capillaries as they help in filtration of blood and remove the nitrogenous wastes from the body in the form of urine.
Question:How does the plant get rid of excretory products? [CBSE 2009]
Answer:
Excess oxygen and carbon dioxide removed through stomata.
Plant waste products are also removed by:
- Storage in cellular vacuoles
- Storage in leaves that fall off
- Storing as resins and gums in old xylem
- By excreting into the soil around them.
Question:Tabulate two differences between renal artery and renal vein. [CBSE 2009]
Answer:
Renal Artery
- Blood in renal artery contains glucose, oxygen and cellular waste products.
- It takes blood towards the kidney.
Renal Vein:
- Blood in renal vein is filtered, and is free from cellular waste and any other impurities.
- It takes blood away from the kidney towards the heart.
Question:Draw a well labelled diagram of stomata. List two functions of stomata. [CBSE 2011]
Answer:
The function of stomata are:
(a) Help in the exchange of gases like carbon dioxide and oxygen from the leaves of the plants.
(b) Help in the transport of water, minerals and food materials in plants by transpiration.
(c) Transpiration occurring through stomata on leaves helps in cooling of leaf surface.
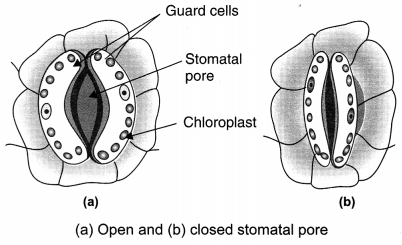
Question: Plants absorb water from the soil. Explain how does the water reach the tree top? [CBSE 2014]:
Answer:
There are two ways for the transport of water in plants:
(а) By root pressure: The cells of root in contact with soil actively take up ions which creates a difference in ion concentration between the root and the soil. Water moves into the root from the soil to eliminate this difference, creating a column of water that is steadily pushed upwards.
(b) By transpiration pull: Loss of water from stomata by transpiration gets replaced by the xylem vessels in the leaf which creates a suction to pull water from the xylem cells of the roots. This strategy is used during day time and helps to transport water to the highest points of the plant body.
Question: State the function of the following in the alimentary canal.
(a) Liver
(b) Gallbladder
(c) Villi [CBSE2014]
Answer:
(a) Liver: Helps in detoxification of harmful chemicals. Produces bile juice which helps in digestion of fats.
(b) Gall bladder: Helps in the storage of bile juice released from the liver.
(c) Villi: Helps to increase the surface area of the small intestine and aid in absorption of the digested nutrients.
Question: Explain the role of mouth in digestion of food. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
The mouth plays an important role in digestion because
- The teeth present in the mouth crush the food into small pieces.
- Tongue helps in thorough mixing of food with saliva and to swallow the food.
- Saliva secreted in mouth contains an enzyme called salivary amylase which helps to break down the starch into maltose.
Question: What are the functions of gastric glands present in the wall of the stomach?
Answer:
The functions of gastric glands present in the wall of the stomach are:
- Produce pepsin enzyme that digests proteins.
- Secrete mucus which protects the inner lining of stomach from the action of acids
Question: Name the energy currency in the living organisms. When and where is it produced? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
The energy currency in the cells is Adenosine triphosphate (ATP). It is produced in mitochondria during respiration and in chloroplasts during photosynthesis in plants.
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Long Answer Type
Question: Draw the sectional view of human heart and label the following parts given below:
(a) Chamber where oxygenated blood from lungs is collected
(b) Largest blood vessel in the body
(c) Muscular wall separating right and left chambers
(d) Blood vessel that carries blood from heart to the lungs [CBSE 2010]
OR
(a) Part which receives deoxygenated blood from vena cava
(b) Part which sends deoxygenated blood to lung through pulmonary artery
(c) Part which receives oxygenated blood from lungs
(d) Part which sends oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through aorta [CBSE 2012]
OR
(a) the chamber of heart that pumps out deoxygenated blood
(b) the blood vessel that carries away oxygenated blood from the heart
(c) the blood vessel that receives deoxygenated blood from the lower part of our body [CBSE 2010, 2011, 2012]
Answer:
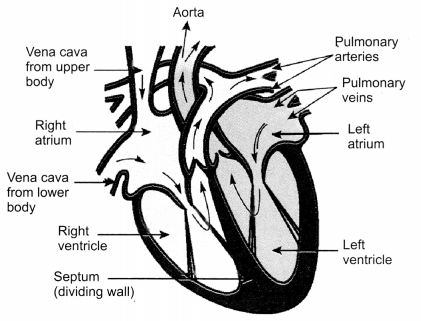
(а) Chamber where oxygenated blood from lungs is collected – Left atrium
(b) Largest blood vessel in the body – Aorta
(c) Muscular wall separating right and left chambers – Septum
(d) Blood vessel that carries blood from heart to the lungs – Pulmonary artery
OR
(а) Part which receives deoxygenated blood from vena cava – Right atrium
(b) Part which sends deoxygenated blood to lung through pulmonary artery – Right Ventricle
(c) Part which receives oxygenated blood from lungs – Left atrium
(d) Part which sends oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through aorta – Left Ventricle
OR
(а) the chamber of heart that pumps out deoxygenated blood – Right Ventricle
(b) the blood vessel that carries away oxygenated blood from the heart – Aorta
(c) the blood vessel that receives deoxygenated blood from the lower part of our body – Inferior Vena cava
Question: Explain how deoxygenated blood travels from body to lung for purification. Draw well labelled diagram in support of your answer. [CBSE 2011]
Answer:
The deoxygenated blood from the various parts of the body is collected by the veins which transport the blood to the heart through the vena cava. Vena cava pours the deoxygenated blood in the right atrium of the heart. The right atrium contracts and the blood moves into the right ventricle. On contraction of the right ventricle the deoxygenated blood is transported to the lungs through the pulmonary artery for purification.
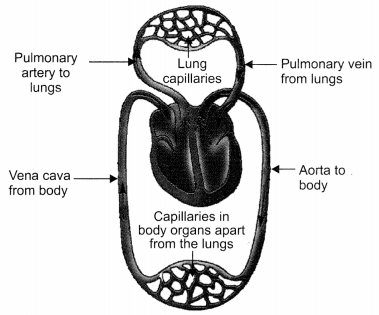
Schematic representation of transport and exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
Question: Draw a diagram of excretory unit of human kidney and label the following:
(a) Bowman’s capsule
(b) Glomerulus
(c) Collecting duct
(d) Renal artery [CBSE 2011, 2012]
Answer:
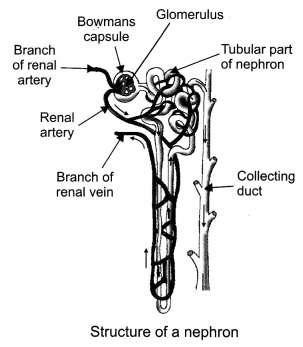
Question: Explain the process of breathing in man. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Air enters the body after getting filtered by fine hairs and mucus in the nostrils.
The air then passes through trachea (present in throat) into the lungs. The trachea divide into bronchi which enter the lungs and divide further into bronchioles which finally terminate in balloon-like structures called alveoli which have a rich supply of blood vessels and help in exchange of gases.
During inhalation (breathing in), the volume of the chest cavity becomes larger as the ribs get lifted and diaphragm gets flattened. Air gets sucked into the lungs and fills the expanded alveoli. The blood brings carbon dioxide from the rest of the body to the alveoli and exchanges it for oxygen to be transported to all the cells in the body.
During exhalation (breathing out), the volume of the chest cavity becomes smaller as the ribs get relaxed and diaphragm moves upward (relaxes). Air rich in carbon dioxide gets pushed out of the lungs to come out through the nostrils.
Question: How do carbohydrates, proteins and fats get digested in human beings?
Answer:
An enzyme called salivary amylase is present in the saliva produced in the mouth. Salivary amylase helps in the breakdown of carbohydrates into maltose in the mouth.
The proteins get digested initially by the pepsin enzyme in the stomach and then by the enzymes present in the pancreatic juice secreted into the small intestine. The fats are broken down into small globules by the bile salts present in the bile juice secreted into the small intestine. This helps in increasing the efficiency of fat digesting enzymes.
The intestinal juice secreted by the walls of the small intestine help to complete the digestion of carbohydrates into glucose/monosaccharide, digestion of proteins into amino acids and the digestion of fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
Question:The gall bladder of a patient is removed when a stone was observed in the gall bladder. Which kind of nutrient in the diet should be absent from the diet given to the patient?
Answer:
The gall bladder release bile juice which helps in the digestion of fats in the human beings. So, the patient should be advised a diet free from fats during the treatment process, as the digestion of fats will be most affected due to removal of gall bladder.
Question:Describe the alimentary canal of man. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Mouth: Helps in intake of whole food.
Teeth: Helps in chewing and grinding of food.
Tongue: Helps in tasting food + rolling food + swallowing food.
Salivary glands: Secrete saliva and mucus. The enzyme called salivary amylase is present in saliva which breaks down the complex starch into sugar.
Oesophagus (food pipe): Food moves towards stomach through oesophagus by rhythmic contraction of its muscles called as peristaltic movements or peristalsis.
Stomach: Muscular walls of stomach help in mixing food thoroughly with digestive juices. Stomach has gastric glands which secrete gastric juice containing pepsin for digestion of proteins, hydrochloric acid for creating acidic medium and mucus to protect inner lining of stomach from acid.
Small Intestine: Digestive juices like pancreatic juice, bile juice and the intestinal juices are secreted in the small intestine to help to complete the process of digestion. After digestion, the nutrients are absorbed by the villi present in the walls of the small intestine.
Large intestine: The unabsorbed food is sent into the large intestine where more villi absorb water from this material and remove the wastes through the anus by egestion. The exit of this waste material is regulated by the anal sphincter.
Question:(а) Why are resins and gums released by plants?
(b) What are the ways in which plants get rid of their waste products?
Answer:(a) Resins and gums are the excretory products of the plants.
(b) Plants remove excess oxygen and carbon dioxide through stomata, excess water by transpiration through stomata and other waste products by storage in cellular vacuoles, leaves that fall off, storage as resins and gums in old xylem or by excreting into the soil around them.


