We have provided you with Extra and Important Questions from Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination. This Extra and Important Questions will help you to score 100% in your Board Exams. These extra questions will be helpful to revise the important topics and concepts.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.
Table of Contents
Control and Coordination Class 10 Important Questions with Answers Science Chapter 7
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Very Short Answer Type
Question:
Define ‘reflex action’. [CBSE 2009]
Answer:
It is an automatic, spontaneous and an immediate involuntary response to a stimulus controlled usually by the spinal cord. e.g. knee jerk movement.
Question:
Name the largest cell in the human body. [CBSE 2003]
Answer:
Nerve cell (Neuron).
Question:
Name a plant hormone which promotes growth in plants. [CBSE 2008]
Answer:
Auxin is a plant hormone that promotes growth and cell elongation in plants.
Question:
State one function each of pons and cerebellum.
Answer:
Pons: Regulates rate of respiration
Cerebellum: Maintains equilibrium of the body during walking, jumping, etc.
Question:
Name a plant hormone that inhibits growth. Write its one more function. [CBSE 2014]
Answer:
Abscisic acid inhibits growth in plants. It also causes closure of stomata during water stress.
Question:
A potted plant is made to lie horizontally on the ground. Which part of the plant will show:
(i) Positive geotropism
(ii) Negative geotropism [CBSE 2010]
Answer:
(i) Roots will shows positive geotropism.
(ii) Shoots will show negative geotropism.
Question:Name a gaseous plant hormone. Give its role.
Answer:
Ethylene is a gaseous hormone. It regulates fruit ripening.
Question:
How many spinal and cranial nerves are present in human body?
Answer:
Spinal nerves = 31 pairs
Cranial nerves = 12 pairs
Question:
What are meninges?
Answer:
The three membranes which cover the brain to protect it are called meninges.
Question: Name two tissues that provide control and coordination in multicellular animals. [CBSE 2009]
Answer:
Muscular tissues and nervous tissue.
Question:
Name the hormone, the secretion of which is responsible for dramatic changes in appearance in girls and boys when they approach 10-12 years of age. [CBSE 2008]
Answer:
Testosterone released from testes in males, estrogen released from ovaries in females.
Question: Give an example of plant hormone that promotes growth. [CBSE 2008]
Answer:
Auxin
Question:
What are plant hormones? [CBSE 2008]
Answer:
The chemical substances produced in plants which help in the growth and development of plant, its tissues and other plants.
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Short Answer Type
Question:
Name the hormones reponsible for regulation.
(i) Metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins
(ii) Balance of calcium and phosphate
(iii) Blood pressure
(iv) Water and electrolyte balance. [CBSE 2007]
Answer:
(i) Thyroxin
(ii) Parathyroid hormone
(iii) Adrenaline
(iv) Vasopressin
Question:
What is an association neuron?
Answer:
Association neurons are present in cortex part of spinal cord between the sensory neuron and motor neuron. It helps to interconnect the signals between the sensory neuron and motor neuron by forming synapse with axon of sensory neuron and dendrite of motor neuron.
Question: Explain how a squirrel responds a dangerous situation with help of its hormonal system.
Answer:
When a squirrel perceives a dangerous situation, adrenaline hormone is released in its blood which increases its heart beat and blood supply to tissues. This provides energy to its cells and tissues at a faster rate and enables it to run away from emergency situation.
Question:
How are sensory neurons different from motor neurons?
Answer:
Sensory neurons take information from receptors and transmit the impulses towards central nervous system. Motor neurons carry message from control nervous system to the muscle, gland or an organ to enable it to respond.
Question:
Lable the parts (a), (b), (c) and (d) and show the direction of flow of electrical signals in the given figure.
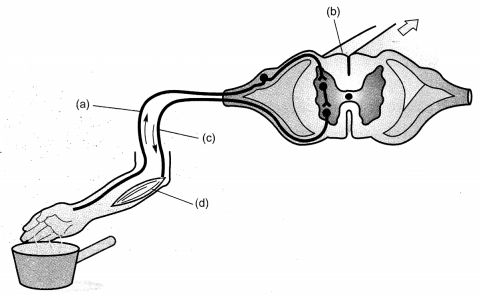
Answer:
(a) Sensory neuron
(b) Spinal cord (part of CNS)
(c) Motor neuron
(d) Effector (Muscle)
Question: How do we detect smell of hot spicy food from a distance?
Answer:
We have olfactory receptors in our nose which detect the smell of hot spicy food.
This information is transmitted by nerve impulse to olfactory lobes of forebrain which interpret the information.
Question:
Why do tendrils coil around hard objects or support?
Answer:
The tendrils coil around hard objects or support due to a stimulus of touch (thigmotropism) which causes less growth on the side in contact with support than the side which is away from it. This unequal growth of two sides of tendril makes it coil around the support.
Question:
How are the brain and spinal cord protected from mechanical shock?
Answer:
Brain is present in a bony box called cranium (skull), spinal cord is protected by vertebral column. The cerebrospinal fluid present around the brain and spinal cord protect it from mechanical shock.
Question:
How does feedback mechanism regulate the hormone action? Explain with the help of an example.
Answer:
The presence or absence of a particular hormone can regulate its further formation with the help of a regulatory mechanism called feedback mechanism.
Example: Hypothalamus regulates thyroxin levels in blood by secreting thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). If the thyroxine levels increases then hypothalamus stop secreting TSH in order to reduce the production of thyroxine from thyroid gland.
Low levels of thyroxin in blood again switches on the release of TSH from hypothalamus to increase levels of thyroxin in blood.
Question:
What are the different types of neurons and their functions in the human body?
Answer:
There are mainly three types of neurons:
- Sensory neuron: They transmit information from receptors towards the central nervous system.
- Motor neuron: They transmit information from the central nervous system to effectors like muscles or glands.
- Relay neuron: It serves as a link between the sensory and the motor neurons in the brain or spinal cord.
Question: Answer the following:
(a) Which hormone is responsible for the changes noticed in females at puberty?
(b) Dwarfism results due to deficiency of which hormone?
(c) Blood sugar level rises due to deficiency of which hormone?
(d) Iodine is necessary for the synthesis of which hormone? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
(a) Oestrogen
(b) Growth hormone
(c) Insulin
(d) Thyroxin
Question:
Answer the following:
(a) Name the endocrine gland associated with brain.
(b) Which gland secretes digestive enzymes as well as hormones?
(c) Name the endocrine gland associated with kidneys.
(d) Which endocrine gland is present in males but not in females? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
(a) Pituitary
(b) Pancreas
(c) Adrenal gland
(d) Testes
Question: What is a tropic movement? Explain with an example. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
The directional movements caused in plants due to an external stimuli are called tropic movements.
Example: During phototropism, the shoot bends towards light and show positive phototropism while the roots bend away from light to show negative phototropism.
Question:
What will happen if intake of iodine in our diet is low? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Iodine helps in the synthesis of thyroxin hormone from thyroid gland. Thyroxin hormone is necessary for carbohydrate, proteins and fat metabolism.
Deficiency caused due to low level of iodine in diet might result is a disease called goitre in the person.
Question: Match the terms of Column (A) with those of Column (B)

[NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
(a) (iii)
(b) (iv)
(c) (i)
(d) (ii)
Question: Label the endocrine glands in figure given below.
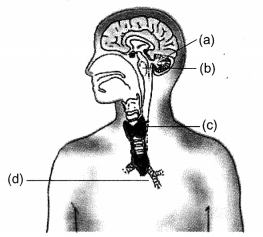
Answer:
(a) Pineal Gland
(b) Pituitary Gland
(c) Thyroid
(d) Thymus
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Long Answer Type
Question: Why is the flow of signals in a synapse from axonal end of one neuron to dendritic end of another neuron but not the reverse? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
The information received by the dendrites of neurons present at receptors is transferred in form of electrical impulse to the cell body, axon and the nerve endings at the ends of axon. At the axonal ends, chemicals are released between junction of two neurons called synapse. The chemical diffuses towards the dendrite of the next neuron where it generates an electrical impulse again. So, the electrical signals change to chemical signals and again to electrical signals for the next neuron.
Since the chemicals Eire released at the axonal ends and absent at dendrite end, the signal travels from axonal end to dendritic end of another neuron but not the reverse i.e., the flow of electrical impulse is unidirectional only.
Question:
Mention one function for each of these hormones:
(a) Thyroxin
(b) Insulin
(c) Adrenaline
(d) Growth hormone
(e) Testosterone
Answer:
(a) Thyroxin: It regulates carbohydrates, fat and protein metabolism.
(b) Insulin: It regulates blood sugar level.
(c) Adrenaline: It increases heart beat rate and supply of blood to various organs.
(d) Growth hormones: It regulates growth and development of an organism.
(e) Testosterone: It controls the bodily features, secondary sexual characters in males during puberty.
Question:
How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
Answer:
Hormones secreted by the endocrine glands are directly poured into the blood stream as they are ductless glands. Blood carries these hormones to specific target tissue or organ where they act and trigger a particular biochemical or physiological activity in response to the stimulus received.
Question:
Differentiate between tropic and nastic movements in plants. [CBSE 2006]
Answer:
Tropic Movements:
- There is directional growth of a plant or part of a plant in response to an external stimulus i.e., direction of stimulus controls direction of growth.
- The effect is more or less permanent.
- It is easily observed in stems and roots of plants.
- It occurs due to unequal growth on the two sides of a stem or root.
- For example, bending of root towards gravity and bending of shoot towards light.
Nastic Movements:
- The growth or movement is independent of the direction of stimulus.
- The effect is temporary and reversible.
- It occurs in specialised parts and organs of plants like leaves and petals of flowers.
- It usually involves alterations in cell volumes.
- For example, folding on leaflets of touch-me-not plant on touching them.
Question:
The level of hormones should be well balanced in human beings in order to maintain the normal functioning of the human body. Explain this statement with two examples.
Answer:
The level of hormones should be balanced in human beings because a deficiency or excess secretion of some hormones can have adverse effects on the human body. For example,
- A deficiency in the secretion of insulin from the pancreas increases the blood sugar level and causes diabetes.
- A deficiency in the secretion of growth hormone causes dwarfism whereas it excess secretion causes gigantism.
Question:
Chemical coordination plays a vital role in the activities of plants. Elaborate.
Answer:
Coordination in human beings is carried out both by the nervous as well as the hormonal system. But, coordination in plants is dependent on the chemicals called as hormones. The hormone auxin and gibberellins help in the growth of the stem. Cytokinins help in cell division. Abscisic acid inhibits growth. Auxin is also involved in the bending of plants towards light.
Question:
The response of the body due to reflex actions is faster than those carried out by secretion of adrenaline in emergency situations. Why?
Answer:
The reflex actions are the result of chemical-electrical impulses which are faster as they move through the nerve cell from one point to another, whereas, hormones are first released in the blood and they have to travel to the target site to bring about the response, which takes more time than reflex actions.
Question:
Rajesh found an old man lying on the road asking for help to take him to the hospital. He took the old man to the hospital where doctor told him that the old man was suffering from paralysis, and his blood sugar levels were high. The doctor told him that they have given the old man some injections to reduce the blood sugar level and thanked Rajesh for his helpful attitude.
On the basis of above passage, answer the following:
(i) What can be the cause of high blood sugar levels in the old man?
(ii) Which part of old man’s body might have been effected that has caused paralysis?
(iii) What values have been shown by Rajesh?
(iv) Which injection might have been given to old man by doctor to lower the blood sugar levels?
Answer:
(i) Diabetes due to the lower levels of insulin hormone in the body.
(ii) Nervous system associated with brain or spinal cord might have been effected.
(iii) Helpful, care for elderly.
(iv) Injections of insulin might have been given by the doctor to the old man to lower his blood sugar levels.


