We have provided you with Extra and Important Questions from Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals. This Extra and Important Questions will help you to score 100% in your Board Exams. These extra questions will be helpful to revise the important topics and concepts.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.
Table of Contents
Metals and Non-metals Class 10 Important Questions with Answers Science Chapter 3
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Very Short Answer Type
Question: A non-metal X exists in two different forms Y and Z. Y is the hardest natural substance, whereas Z is a good conductor of electricity. Identify X, Y and Z.
Answer: ‘X’ is carbon, ‘Y’ is diamond as it is the hardest natural substance and ‘Z’ is graphite as it is good conductor of electricity.
Question: Why does calcium float in water?
Answer: It is because hydrogen gas is formed which sticks to surface of calcium, therefore it floats.
Question: Name a non-metal which is lustrous and a metal which is non-lustrous. Iodine is a nonmetal which is lustrous,
Answer: Lead is a non-lustrous metal.
Question: Which gas is liberated when a metal reacts with an acid? How will you test the presence of this gas?
Answer: Hydrogen gas is formed. Bring a burning matchstick near to it, H2 will burn explosively with ‘pop’ sound.
Question:Name two metals which are both malleable and ductile.
Answer:
Silver and gold.
Question:Name the non-metal which is a liquid.
Answer:
Bromine.
Question:Expand PVC.
Answer:
Polyvinyl chloride.
Question: What is the valency of silicon with atomic number 14?
Answer: Its valency is equal to 4.
Question: What is the valency of phosphorus with atomic number 15?
Answer: Phosphorus has valency 3.
Question: What is the valency of an element with atomic number 35?
Answer: Its valency is 1.
Question: Arrange the following metals in the decreasing order of reactivity: Na, K, Cu, Ag.
Answer: K > Na > Cu > Ag
Question:Name two metals which can be cut with a knife.
Answer:
Lithium, sodium, potassium
Question: An element forms an oxide A2O3 which is acidic in nature. Identify A as a metal or non-metal. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Oxides of non-metals are acidic in nature while those of metals are basic in nature. Hence, A must be a non-metal.
Question: Why does calcium float in water?
Answer:
Calcium reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide and hydrogen. Bubbles of hydrogen gas stick to the surface of calcium, hence it floats.
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Short Answer Type
Question: What is cinnabar? How is metal extracted from cinnabar? Explain briefly.
Answer: Cinnabar is HgS.
Mercury is obtained by roasting cinnabar. HgO formed is thermally unstable and gives mercury.
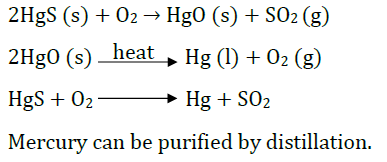
Question: (a) Write the electron dot structures for potassium and chlorine.
(b) Show the formation of KCl by the transfer of electrons.
(c) Name the ions present in the compound, KCl.
Answer:
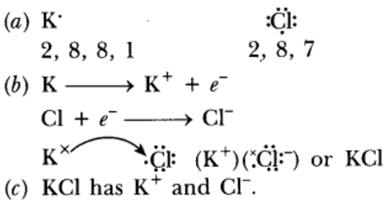
Question: (a)State the electron-dot structure for calcium and sulphur.
(b) Show the formation of CaS by the transfer of electrons.
(c) Name the ions present in this compound CaS. Atomic number of Ca = 20, O = 16.
Answer:
Question: Suggest a method of reduction for the following metals during their metallurgical processes:
(i) metal ‘A’ which is one of the last, second or third position in the reactivity.
(ii) metal ‘B’ which gives vigorous reaction even with water and air.
(iii) metal ‘C’ which is kept in the middle df activity series.
Answer: (i) ‘A’ can be obtained by chemical reduction using carbon or carbon monoxide as reducing agent.
(ii) ‘B’ can be obtained by electrolytic reduction.
(iii) ‘C’ can be reduced by reducing agent like ‘Al’.
Question:Name two metals which react violently with cold water. Write any three observations you would make when such a metal is dropped into water. How would you identify the gas evolved, if any, during the reaction? [CBSE 2008]
Answer:
Sodium, Potassium
When these metals are dropped in water, bubbles will be evolved due to evolution of hydrogen gas.
The gas will catch fire and the solution will be alkaline, i.e., it will turn red litmus blue.
Question:State reasons for the following:
(i) Electric wires are covered with rubber-like material.
(ii) From dilute hydrochloric acid, zinc can liberate hydrogen gas but copper cannot.
Answer:
(i) It is because rubber is an insulator and does not allow current to flow through it.
(ii) Zinc is is placed above hydrogen in the reactivity series of metals while copper is placed below it. Metals placed above hydrogen can displace hydrogen from water and acids while those below it cannot. Therefore, zinc can displace hydrogen from dilute HCl whereas copper cannot.
Question:Give the formulae of the stable binary compounds that would be formed by the combination of the following pairs of elements.
(a) Mg and N2
(b) Li and O2
(c) Al and Cl2
(d) K and O2
Answer:
(a) Mg3N2
(b) Li2O
(c) AlCl3
(d) K2O
Question:Compound X and aluminium are used to join railway tracks.
(a) Identify the compound X
(b) Name the reaction
(c) Write down its reaction. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
(a) Compound X must be iron (III) oxide, Fe2O3.
(b) The reaction is known as ‘thermite reaction’ or ‘aluminothermy’.
(c) The reaction is carried out by igniting the mixture with a Mg-ribbon.![]()
Question:Name two metals which will displace hydrogen from dilute acids, and two metals which will not.
Answer:
Zinc and magnesium can displace hydrogen from dilute acids whereas copper and silver cannot. The metals lying above hydrogen in the reactivity series can displace hydrogen on reaction with dilute acids.
Question:During extraction of metals, electrolytic refining is used to obtain pure metals,
(a) Which material will be used as anode and cathode for refining of silver metal by this process?
(b) Suggest a suitable electrolyte also,
(c) In this electrolytic cell, where do we get pure silver after passing electric current? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
In the electrolytic refining of impure silver metal:
(a) A rod of impure silver is used as anode while that of pure silver as cathode.
(b) The electrolyte is a water soluble salt of silver, for example silver chloride or silver nitrate.
(c) On passing current, pure silver gets deposited at the cathode. It can be scrapped off later on.
Question:Give reason for the following:
(i) Iron grills are frequently painted.
(ii) Gold ornaments retain their lustre even after several years of use.
Answer:
(i) Iron metal easily gets rusted by air containing moisture and oxygen. Therefore, iron grills are frequently painted with rust proof paints.
(ii) Gold is a noble metal and is not affected by chemicals or by air. Therefore, gold ornaments retain their lustre even after several years.
Question:Name two metals which can be used to reduce metal oxides to metal.
Answer:
(i) Aluminium (Al)![]()
(ii) Magnesium (Mg)![]()
Question: (i) Write down the electronic configuration
of magnesium and oxygen.
(ii) Give two general properties of the compound formed by combination of magnesium and oxygen.
(iii) Show the formation of this compound by the transfer of electrons. (Board Term 1,2014)
Answer:
(i) Atomic number of magnesium (Mg) = 12
∴ Its electronic configuration = 2, 8, 2
Atomic number of oxygen = 8
Electronic configuration of oxygen = 2, 6
(ii) Magnesium (Mg) reacts with oxygen (O2) to form magnesium oxide (MgO).
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
Properties of MgO are :
(a) It involves ionic bonding.
(b) It has high melting point due to strong electrostatic forces of attraction between Mg2+ and O2- ions.
(iii) In the formation of magnesium oxide, two electrons are transferred from magnesium atom to oxygen atom as represented :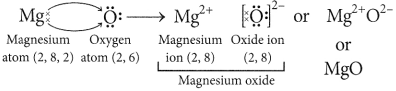
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Long Answer Type
Question: Give reasons for the following observations:
(i) Ionic compounds in general have high melting and boiling points.
(ii) Highly reactive metals cannot be obtained from their oxides by heating
them with carbon.
(iii) Copper vessels get a green coat when left exposed to air in the rainy season.
Answer. (i) Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points due to strong force of attraction between oppositely charged ions.
(ii) It is because these metals themselves are strong reducing agents. Therefore, cannot be reduced by reducing agent like carbon.
(iii) Copper vessels react with CO2, O2 and moisture to form green-coloured basic copper carbonate
[CuCO3.Cu(OH)2].
Question: State reasons for the following observations:
(i) The shining surface of some metals becomes dull when exposed to air for a long time.
(ii) Zinc fails to evolve hydrogen gas on reacting with dilute nitric acid.
(iii) Metal sulphides occur mainly in rocks but metal halides occur mostly in sea and lake waters.
Answer.
(i) It is because metal reacts with substances present in atmosphere to form surface compounds which make it dull.
(ii) It is because dil. HNOs is an oxidising agent therefore zinc gives NO and notH2 with dil. HNOs.
(iii) It is because sea water contains sodium chloride due to which metal halides are formed, whereas sulphur is found below rocks. Therefore, metal – sulphides are formed in rocks.
Question: State reasons for the following:
(i) Electric wires are covered with rubber like material.
(ii)From dilute hydrochloric acid, zinc can liberate hydrogen gas but copper cannot.
(iii) Sulphide ore of a metal is first converted to its oxide to extract the metal from it.
Answer.
(i) It is because rubber is an insulator and does not allow current to flow through it.
(ii) Zinc is more reactive than hydrogen. Therefore, it can displace hydrogen from dilute HCl whereas copper cannot, because it is less reactive than hydrogen. ,
(iii) It is because it is easier to reduce oxide ore as compared to sulphide ore.
Long Answer Type Questions [5 Marks] -Year 2009
Question:(a) What is meant by corrosion? Name any two methods used for the prevention
of corrosion.
(b) Suppose you have to extract metal M from its enriched sulphide ore. If M is in the middle of the reactivity series, write various steps used in extracting this metal.
Answer. (a) Corrosion is a process in which metal reacts with substances present in the environment to form surface compounds.
Prevention:
(i) Galvanisation is a process to prevent corrosion of iron.
(ii)Electroplating is also used to prevent corrosion.
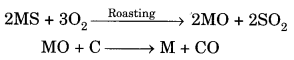
(b)(i) Concentration of ores: Sulphide ore will be concentrated by froth- floatation process. Sulphide ore will be collected in froth whereas gangue will be left behind.
(ii) Roasslng: Sulphide ore is heated strongly in the presence of O2 to form metal oxide and sulphur dioxide.
2MS + 3O2 ————- ► 2MO + 2SO2
(iii) Reduction: MO reacts with carbon (acts as reducing agent) to form metal and CO.
MO + C —-> M + CO
(iv) Electrolytic refining: Impure metal ‘M’ is purified by electrolytic refining. Impure metal is taken as anode, pure metal is taken as cathode, soluble salt of metal is taken as electrolyte. Impure metal forms metal ions which gain electrons and form pure metal at cathode.
Question: (a) How can the metals at the top of the reactivity series be extracted from their ores? Explain with an example.
(b) Name any one alloy made from
(i) a metal and a non-metal, and
(ii) two metals.
Answer: (a) These metals are extracted by electrolytic reduction, e.g. aluminium is obtained from bauxite by electrolytic reduction.
(b) (i) Steel is made up of iron and carbon.
(ii) Brass is made up of copper and zinc.
Question: With the help of a suitable example, explain how ionic compounds are formed. State any three general properties of ionic compounds.
Answer: Ionic compounds are formed by transfer of electrons from metal to non-metals, e.g.
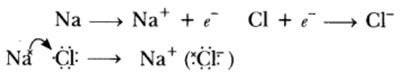
General Properties:
(i) They are the solids having high melting point.
(ii) They are soluble in water.
(iii) They conduct electricity in molten state as well as in aqueous solution.
Question: (a) Explain with an example how the metal (X) which is low in reactivity series and metal (Y) which is high in the reactivity series are obtained from their compounds by reduction process.
(b) Write the electronic configurations of sodium and chlorine. Show the formation of sodium chloride from sodium and chlorine by the transfer of electrons.
(c) List any two observations when a highly reactive metal is dropped in water.
Answer: (a) ‘X’ is obtained by chemical reduction. ‘Y’ is obtained by electrolytic reduction.
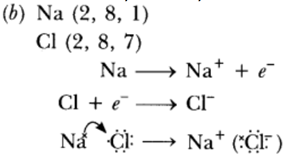
(c) (i) Metal will catch fire.
(ii) Alkali solution is formed which turns red litmus blue.
Question: (a) The reaction of metal (X) with ferric oxide is highly exothermic. Metal
(X) is obtained from its oxides by electrolytic reduction. Identify (X) and write its reaction with ferric oxide.
(b) Give reason to justify that aluminium oxide is an amphoteric oxide. Also, give another example of amphoteric oxide.
(c) Mention constituent metals present in bronze.
Answer: (a) ‘X’ is ‘Al’
2Al + Fe2O3 → Al2O3 + 2Fe
(b) AI2O3 reacts with acid as well as base therefore it is amphoteric oxide.
AI2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O
AI2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2
Zinc oxide is also an amphoteric oxide.
(c) Bronze contains’ copper and tin.
Question:(i) Given below are the steps for extraction of copper from its ore. Write the reaction involved.
(a) Roasting of copper (I) sulphide.
(b) Reduction of copper (I) oxide with copper (I) sulphide.
(c) Electrolytic refining.
(ii) Draw a neat and well labelled diagram for electrolytic refining of copper. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
(i)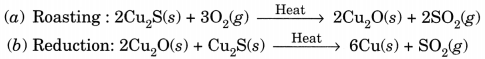
This reaction in which one of the reactants (Cu2S) carries the reduction of the product (Cu2O) is known as auto-reduction.
(c) Reaction taking place in electrolytic refining are:
At cathode (reduction): Cu2+(aq) + 2e– → Cu(s)
At anode (oxidation): Cu(s) → Cu2+ (aq) + 2e–
(ii) Metals like copper, aluminium and zinc are refined by this process.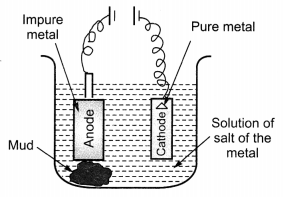
Question:(a) In the formation of compound between two atoms A and B, A loses two electrons and B gains one electron.
(i) What is the nature of the bond between A and B?
(ii) Suggest the formula of the compound formed between A and B.
(b) On similar lines explain the formation of MgCl2 molecule.
(c) Common salt conducts electricity only in the molten state. Why?
(d) Why is melting point of NaCl high?
Answer:
(a) (i) Ionic bond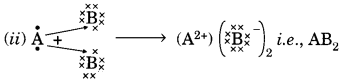
(b) Mg → Mg2+ + 2e–
2Cl + 2e– → 2Cl–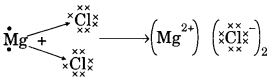
(c) Na+ and Cl– ions are free to move in molten state but not in solid state.
(d) It is due to strong force of attraction between Na+ and Cl–.
Question:Two ores A and B were taken. On heating ore A gives CO2 whereas, ore B gives SO2. What steps will you take to convert them into metals? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Since ore A gives CO2 and ore B gives SO2. Therefore, ores are MCO3 and MS.
A can be obtained
B can be obtained