Case study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 13 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Case Study Questions With answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
Question 1:
An electric motor is a rotating device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy electric motors are used as an important component in electric fans, refrigerators, mixer, washing machines, computers, MP3 players etc. Motor Works on the principle that when a rectangular coil is placed in a magnetic field and current is passed through it, a force acts on the coil which rotates it continuously. When the coil rotates the shaft attached to it also rotates. In this way the electrical energy supplied to the motor is converted into the mechanical energy of rotation.
1.1) When the current is switched on, an electric fan converts :
(a) electrical energy into mechanical energy
(b) chemical energy into mechanical energy
(c) electrical energy into mechanical energy
(d) mechanical energy into electrical energy
Answer: (c) electrical energy into mechanical energy
1.2) In an electric motor, the direction of current in the coil changes once in each
(a) two rotations
(b) one rotation
(c) half rotation
(d) one-fourth rotation
Answer: (c) half rotation
1.3) An electron beam enters a magnetic field at right angles to it. The direction of force acting on the electron beam will be :
(a) to the right
(b) to the left
(c) into the page
(d) out of the page
Answer: (c) into the page
1.4) A magnetic field exerts no force on :
(a) an unmagnetised iron bar
(b) a stationary electric charge
(c) a magnet
(d) an electric charge moving perpendicular to its direction
Answer: (b) a stationary electric charge
1.5) Which of the following has no effect on the size of the turning effect on the coil of an electric motor?
(a) The amount of the current in the coil.
(b) The number of turns in the coil.
(c) The direction of the current in the coil.
(d) The strength of the magnetic field.
Answer: (c) The direction of the current in the coil
Question 2:
An insulated copper wire wound on a cylindrical cardboard tube such that its length is greater than its diameter is called a solenoid. When an electric current is passed through the solenoid, it produces a magnetic field around it. The magnetic field produced by a current-carrying solenoid is similar to the magnetic field produced by a bar magnet. The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of parallel straight lines. The strong magnetic field produced inside a current-carrying solenoid can be used to magnetize a piece of a magnetic material like soft iron when placed inside the solenoid. The strength of the magnetic field produced by a current-carrying solenoid is directly proportional to the number of turns and strength of the current in the solenoid.
(i) The strength of magnetic field inside a long current-carrying straight solenoid is
(a) more at the ends than at the centre
(b) minimum in the middle
(c) same at all points
(d) found to increase from one end to the other.
Answer: (c) same at all points
(ii) The north-south polarities of an electromagnet can be found easily by using
| (a) Fleming’s right-hand rule | (b) Fleming’s left-hand rule |
| (c) Clock face rule | (d) Left-hand thumb rule |
Answer: (c) Clock face rule
(iii) For a current in a long straight solenoid N-and S-poles are created at the two ends. Among the following statements, the incorrect statement is
(a) The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of straight lines which indicates that the magnetic field is the same at all points inside the solenoid.
(b) The strong magnetic field produced inside the solenoid can be used to magnetise a piece of magnetic material like soft iron, when placed inside the coil.
(c) The pattern of the magnetic field associated with the solenoid is different from the pattern of the magnetic field around a bar magnet.
(d) The N- and S-poles exchange position when the direction of current through the solenoid is reversed.
Answer: (c) The pattern of the magnetic field associated with the solenoid is different from the pattern of the magnetic field around a bar magnet.
(iv) A long solenoid carrying a current produces a magnetic field B along its axis. If the current is double and the number of turns per cm is halved, then new value of magnetic field is
| (a) B | (b) 2B | (c) 4B | (d) B/2 |
Answer: (a) B
(v) A soft iron bar is enclosed by a coil of insulated copper wire as shown in figure. When the plug of the key is closed, the face B of the iron bar marked as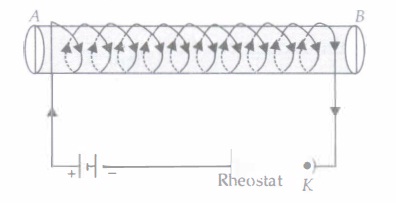
| (a) N-pole | (b) S-pole |
| (c) N-pole if the current is large | (d) S-pole if the current is small |
Answer: (a) N-pole
Question 3:
An electric motor is a rotating device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Electric motor is used as an important component in electric fans, refrigerators, mixers, washing machines, computers, MP3 players, etc.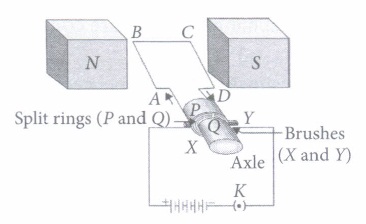
An electric motor consists of a rectangular coil ABCD of insulated copper wire. The coil is placed between the two poles of a magnetic field such that the arm AB and CD are perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field. The ends of the coil are connected to the two halves P and Q of a split ring. The inner sides of these halves are insulated and attached to an axle. The external conducting edges of P and Q touch two conducting stationary brushes X and Y, respectively, as shown in the figure. Commercial motors use an electromagnet in place of a permanent magnet, a large number of turns of conducting wire in the current-carrying coil, and a soft iron core on which the coil is wound.
(i) Choose incorrect statement from the following regarding split rings.
(a) Split rings are used to reverse the direction of current in coil.
(b) Split rings are also known as commutator.
(c) Split ring ii a discontinuous or a broken ring.
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer: (d) Both (a) and (b)
(ii) Which of the following has no effect on the size of the turning effect on the coil of an electric motor?
| (a) The amount of the current in the coil | (b) The direction of the current in the coil. |
| (c) The number of turns in the coil. | (d) The strength of the magnetic field |
Answer: (b) The direction of the current in the coil.
(iii) When current is switched ON, an electric fan converts
| (a) mechanical energy to chemical energy | (b) electrical energy to mechanical energy |
| (c) chemical energy to mechanical energy | (d) mechanical energy to electrical energy. |
Answer: (b) electrical energy to mechanical energy
(iv) In an electric motor, device that makes contact with the rotating rings and through them to supply current to coil is
| (a) axle | (b) brushes | (c) coil | (d) split rings. |
Answer:(b) brushes
(v) In an electric motor, the direction of current in the coil changes once in each
| (a) two rotations | (b) one rotation | (c) half rotation | (d) one-fourth rotation |
Answer:(c) half rotation
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 10 Science Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible
By Team Study Rate

