Case study Questions on Class 9 Science Chapter 4 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Class 9 Science Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure of Atom
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.
In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Structure of Atom Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure of Atom
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1: The maximum number of electrons that are permitted to be assigned to an energy shell of an atom is called the electron capacity of that shell. The distribution of electrons in different orbits or shells is governed by a scheme known as the Bohr-Bury scheme. According to this scheme :
(i) The maximum number of electrons that can be present in any shell is given by the formula 2n2 where n is the number of energy levels.
(ii) The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in the outermost shell is 8. Electrons are filled in the shells in a stepwise manner in increasing the order of energy of the energy shell.
What is the maximum electron capacity of the N shell?
(a) 24 (b) 8 (c) 18 (d) 32
Answer: (d) 32
Identify the element with the configuration K-2, L-8, M-3.
(a) Aluminium (b) Magnesium
(c) Sodium (d) Beryllium
Answer: (a) Aluminium
Which of the following configuration represent sodium?
(a) 2, 8, 4 (b) 2, 8, 5
(c) 2, 3 (d) 2, 8, 1
Answer: (d) 2, 8, 1
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
The given diagrams show the atomic structures of elements X and Y.
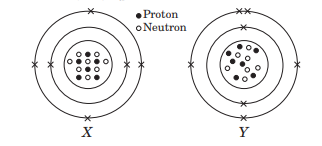
Element X and Y could be _ and _ respectively.
(a) Be and B (b) C and O
(c) F and N (d) C and N
Answer: (d) C and N
Valency of elements X and Y are respectively,
(a) 4 and 3 (b) 2 and 5
(c) 1 and 4 (d) 3 and 4
Answer: (a) 4 and 3
Elements X and Y are
(a) isotopes (b) isoelectronic
(c) isobars (d) isomers.
Answer: (c) isobars
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 2: The mass of an atom is due to the masses of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. The relative masses of protons and neutrons are almost equal to one. Therefore, the atomic mass of an element should be nearly a whole number. But in many cases the atomic masses are fractional. The main reason for these fractional atomic masses is that these elements occur in nature as a mixture of several isotopes. The atomic mass of an element is the average of the atomic masses of these isotopes in the ratio of their proportion of occurrence.
Chlorine occurs in nature in the form of two isotopes with atomic masses 35 u and 37 u in the ratio of 3 : 1 respectively. The atomic mass of chlorine is
(a) 35.5 u (b) 34.5 u (c) 35 u (d) 36 u
Answer: (a) 35.5 u
An element occurs in two isotopic forms with atomic masses 10 and 11. What is the percentage abundance of two isotopes in the sample having an atomic mass of 10.80?
(a) 20, 80 (b) 50, 50 (c) 25, 70 (d) 60, 40
Answer: (a) 20, 80
The fractional atomic masses of elements are due to the existence of
(a) isotopes having different masses
(b) diagonal relationship
(c) equal number of electrons and protons
(d) none of these.
Answer: (a) isotopes having different masses
Case Study 3: The structure of an atom consists of subatomic particles, mainly protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus, which is the central region of an atom. Protons carry a positive charge, while neutrons are electrically neutral. Electrons, on the other hand, are negatively charged particles that orbit around the nucleus in energy levels or shells. The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number, which is unique to each element. The mass number of an atom is the sum of its protons and neutrons. The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average mass of all its naturally occurring isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The arrangement and distribution of these subatomic particles determine the overall stability and properties of an atom.
Which subatomic particles are mainly located in the nucleus of an atom?
a) Protons and electrons
b) Neutrons and electrons
c) Protons and neutrons
d) Protons, neutrons, and electrons
Answer: c) Protons and neutrons
What is the charge of protons?
a) Positive
b) Negative
c) Neutral
d) Variable
Answer: a) Positive
Where are electrons located in an atom?
a) Nucleus
b) Energy levels or shells
c) Protons
d) Neutrons
Answer: b) Energy levels or shells
What determines the atomic number of an atom?
a) Number of electrons
b) Number of protons
c) Number of neutrons
d) Sum of protons and neutrons
Answer: b) Number of protons
What are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons called?
a) Isotopes
b) Ions
c) Elements
d) Electrons
Answer: a) Isotopes
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure of Atom with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 9 Science Structure of Atom Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible
By Team Study Rate

